Pan-African Snake Antivenom
Envenoming by snakes is an important public health problem in Africa, where an estimated 500.000 cases occur annually, resulting in high mortality and morbidity.
A polyspecific Pan-African antivenom has been produced from the plasma of horses immunized with a mixture of the venoms of Echis ocellatus, Bitis arietans and Naja nigricollis, the three most medically important snakes in sub-Saharan Africa.
Snake antivenom immunoglobulins (antivenoms) are the only specific treatment for envenoming by snakebites. Antivenoms can prevent or reverse most of the snakebite envenomings effects, and play a crucial role in minimizing mortality and morbidity. These preparations are included in the WHO List of Essential Medicines and should be part of any primary health care package where snakebites occur
We put 50+ years of experience at your service!
WORKS AGAINST :
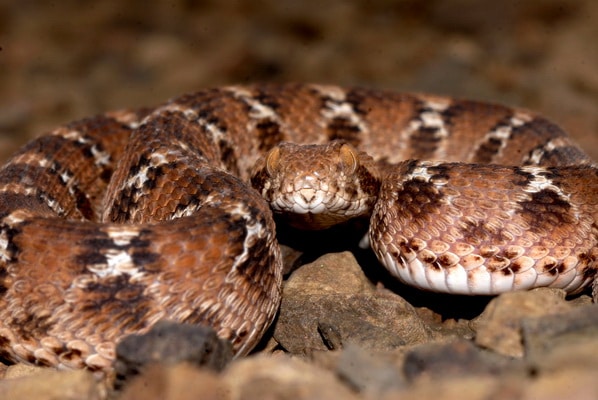
Echis spp.
| White-bellied carpet viper | Echis leucogaster |
| West african carpet viper | Echis ocellatus |
| East african carpet viper |
Echis pyramidum |
Bitis spp.
| Puff adder |
Bitis arietans |
| East african gaboon viper |
Bitis gabonica |
| Butterfly viper / River jack | Bitis nasicornis |
| West african gaboon viper | Bitis rhinoceros |
Naja spp.
| Ashe’s spitting cobra | Naja ashei |
| Katian spitting cobra / Mali cobra |
Naja katiensis |
| Mozambique spitting cobra |
Naja mossambica |
| Black-necked spitting cobra |
Naja nigricollis |
| Red spitting cobra |
Naja pallida |

TRUSTED WORLDWIDE
The Clodomiro Picado Institute produces antivenoms for many Central and South American and European countries. It has developed innovative scientific and biotechnical processes to promote the enhancement of biologicals, both nationally and internationally; it advises countries on the prevention and treatment of snakebites, and also the production and quality control of antivenoms in Central and South America; and it manages collaboration projects for the production of antivenoms specific to countries with scarce resources such as Nigeria, Papua New Guinea and Sri Lanka. In collaboration with the Latin American science and technology development programme (CYTED), the Clodomiro Picado Institute coordinates a network of production centres in Central and South America.
The Institute was involved in the drafting of the WHO Guidelines for the Production, Control and Regulation of Snake Antivenom Immunoglobulins.
“EchiTAb-PLUS-ICP showed to be safe due to the low rates of adverse reactions. This is in line with neutralization studies which have also demonstrated the safety and efficacy of EchiTAb-PLUS-ICP in African viperid envenoming“

Treatment outcomes among snakebite patients in north-west Ethiopia—A retrospective analysis
PLOS Neglected Tropical Diseases, Feb 9, 2022